In this article, we’ll learn how to check and Get SharePoint Farm Build Version in SharePoint 2019, 2016, and 2013 to know What’s the current Cumulative Update installed on SharePoint Farm. Also, we’ll explore the SharePoint Patching Steps.
- 1 SharePoint Farm Build Version
-
2
How to Find SharePoint Farm Build Number and Patch Level?
- 2.1 Get SharePoint farm build version using SharePoint Detector Google Extension
- 2.2 Get SharePoint Build Number PowerShell
- 2.3 Get SharePoint Farm Build Version using Central Administration
- 2.4 Get SharePoint updates that already installed on SharePoint Farm
- 2.5 Get SharePoint Database Schema Versions
- 3 Get SharePoint Farm Build Version In SQL Server
- 4 What’s the current Cumulative Update installed on SharePoint Farm?
-
5
Cumulative Update Vs Service Pack Vs Public Update in SharePoint Server
- 5.1 What’s SharePoint Cumulative Updates (CUs)?
- 5.2 What’s SharePoint Server Packages (also known as “Uber” Packages)?
- 5.3 What’s SharePoint Public Updates (PUs)?
- 5.4 What’s Critical On Demand Fix (COD)?
- 5.5 What’s SharePoint Service Pack?
- 5.6 What’s SharePoint Feature Pack?
- 5.7 What’s the difference between Feature Pack and Service Pack?
- 6 Why you should patch your SharePoint farm?
- 7 When you should patch your SharePoint farm?
- 8 Prerequisites for Installing New Update In SharePoint Farm
- 9 Install new Cumulative Update for a SharePoint Farm
- 10 Check SharePoint Upgrade and Migration Status
- 11 Install new Cumulative Update in SharePoint 2016
Before you decide to patch a SharePoint farm with a new Cumulative Update / Service Pack / Public Update. you should first check the below important questions:
- What’s the current Cumulative Update installed on SharePoint Farm?
- What’s the difference between Cumulative Update, Service Pack, Public Update?
- Why and When you should patch your farm?
- What’re the prerequisites for installing a new Cumulative Update?
- How can you install a new Cumulative Update, Service Pack, and PU in SharePoint Server?
- Patching SharePoint Farm Step by Step.
In this section, we’ll show how to get the SharePoint farm build version through the following:
- Get SharePoint farm build version using SharePoint Detector Google Extension.
- Get SharePoint farm build version using Central Administration.
- Get SharePoint build number PowerShell.
- Get Products and Patches build numbers that already installed on the farm.
- Get SharePoint Database Schema Version.
- Get SharePoint farm build version through SQL Server:
You can easily get the latest cumulative update that already installed on your SharePoint farm or in other farm using my SharePoint Detector google extension.
- No need to access the Central Administration.
- No need to run PowerShell Script.
- No need to log in to your SharePoint site.
Just find the build number and the latest cumulative update for your farm at the push of a button using SharePoint Cumulative Update Detector.

Note: This extension is now down for maintenance, the new version will be published soon.
To Get SharePoint Build Number using PowerShell, you should do the following:
Steps
- Open SharePoint Management Shell as administrator.
- Run the following Cmdlet’
(Get-SPFarm).BuildVersion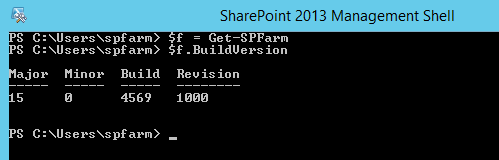
To Get SharePoint Farm Build Version using Central Administration, you should do the following:
Steps
- Open Central Administration > System Settings > Manage Servers in this farm.
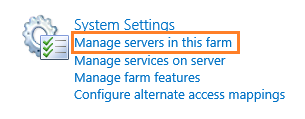
- Below Farm Information > Check the Configuration database version that is the farm patch level of the farm (Build Farm Version).
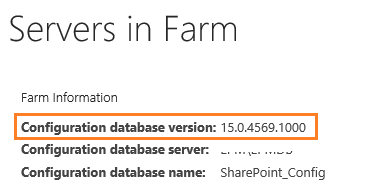
Note: In some cases, this version number is not updated after applying a new Cumulative Update, so it’s not considered a trusted version number. For more details check SharePoint patching demystified
You can also check the SharePoint Products and Patches build numbers and its status that you have installed on SharePoint farm by doing the following:
Steps
- Go to Upgrade and Migration > Check product and patch installation status.
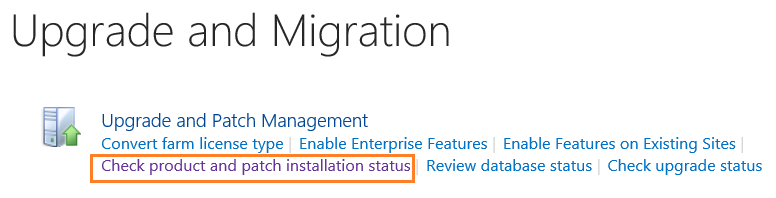
- You could check all the installed products in the whole farm or on a specific server.
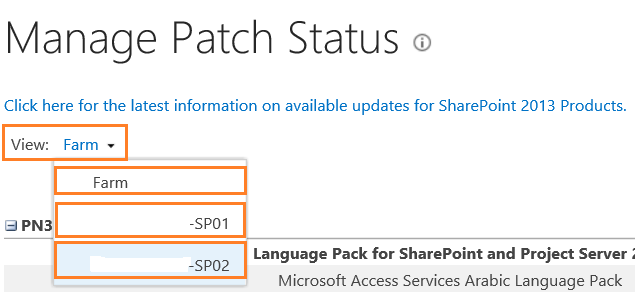
- Check the status and version columns for all installed Products/Patches.
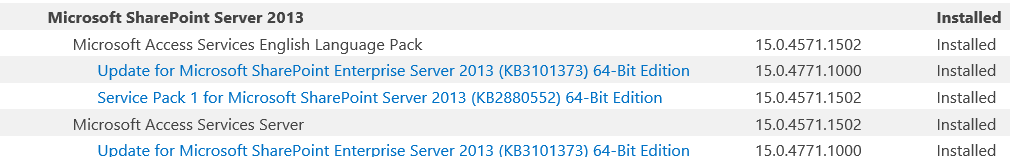
You might also like to read Product/patch installation or server upgrade required
To get SharePoint Database Schema Versions, you should do the following:
- Central Administration > Upgrade and Migration > Review Database Status.

- Manage Database Upgrade Status > Click on Content Database name.
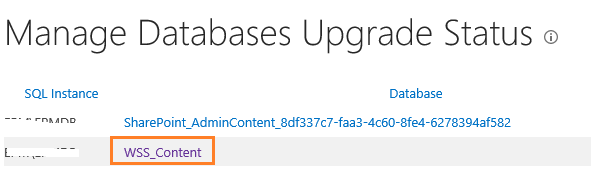
- Get the database Schema Versions.
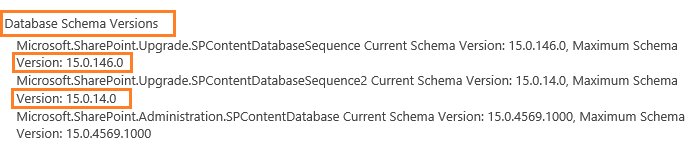
You might also like to read This content database has a schema version which is not supported in this farm
You can also get SharePoint Farm Build Version from “dbo.Versions” table as the following:
- Open SQL Server Management Studio.
- Open the Content Database > Versions Table.
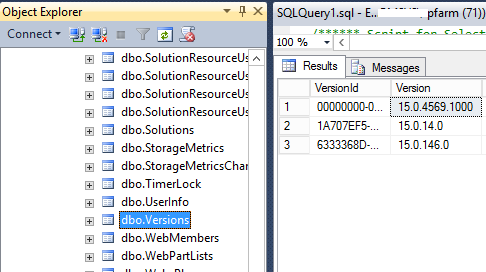
- The Farm build number is the corresponding value of versionID start with ‘0000000-000’ that is ‘15.0.4569.1000‘.
- The version table also shows the Database Sequence build number that is ‘15.0.14.0‘ & ‘15.0.146.0‘.
You might also like to read Database running in compatibility range upgrade recommended
After you get SharePoint farm build version, you’ll be able now to get its corresponding release name by browsing the below links based on your SharePoint version.
- SharePoint 2010 Build Version Numbers.
- SharePoint 2013 Build Version Numbers.
- SharePoint 2016 Build Version Numbers.
- SharePoint 2019 Build Version Numbers.
Then search for the corresponding release with the farm build number as shown below:
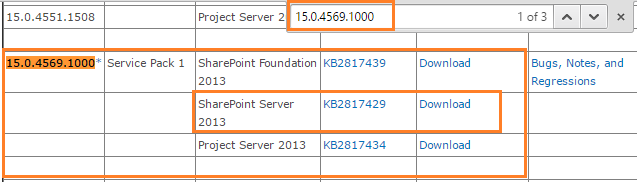
In my case, the related release of my farm build number ‘15.0.4569.1000’ was SharePoint 2013 Service Pack 1.
In this section, we’ll learn What’s the difference between Cumulative Update, Service Pack, Public Update, etc?
- The SharePoint Cumulative Update Is an update accumulated only for a particular component in the SharePoint product like (Excel Service, Search, …., etc. ).
- It includes fixes for problems that have been reported by the customer in the context of support cases.
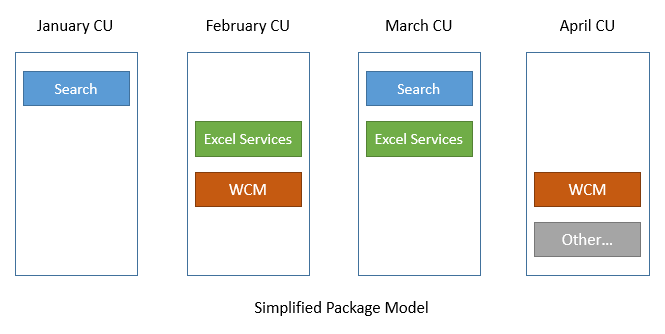
- The “Uber” packages which are usually released with each CU not only include patches for the components updated in the current CU, but also all patches released for other components of the product. So they are very similar to a mini service pack.
- In the past, Microsoft always shipped a “Uber” package with every CU. But August 2014 CU was the first CU where no ” Uber” package was released.
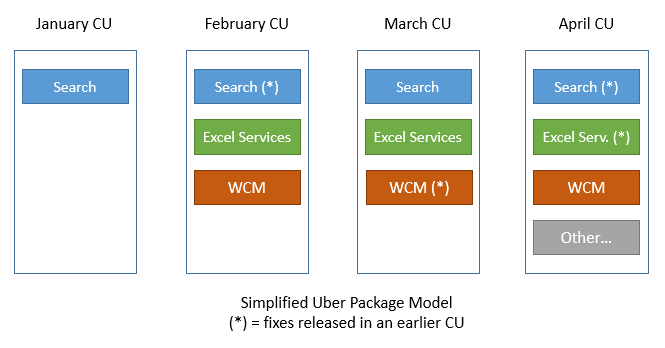
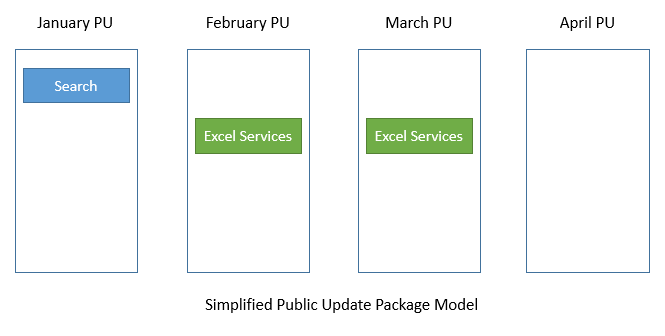
- Public Updates are also cumulative updates – but only include those packages which include updates that should be distributed to all customers. Public updates are either security fixes or other fixes that are recommended to be installed by all customers as they address issues that affect many users. A public update is always a subset of a CU, and CU is a subset of Uber Package.
- SharePoint PUs are cumulative – so installing the Excel Services PU from March will also apply the changes to Excel Services included in February PU and also all other fixes which were added to the same package in previous CUs. But as March PU does not ship any changes for the Search component it will be required to also install January PU to ensure that your system is properly patched with all public updates.
What’s Critical On Demand Fix (COD)?
- Critical On Demand Fix (COD) is a fix that provided only to a small number of customers affected by a critical problem directly through Microsoft Support to provide quick relief.
- The code change in the COD will be included in one of the next CUs, and it is advised to install that CU on top of the COD as soon as it has been released.
- Service Pack is a combination of previously released fixes, fixes that have only been released in the context of the service pack and potentially new functionality added to the product.
- Each service pack sets a new patch baseline while CUs don’t set such a baseline. The patch baseline is the starting point for patching. Looking at the second picture above (the one explaining the “Uber” packages) you can see that the CU only included fixes for Search but not for any other component.
- The reason is that no fixes have been released for other components since the patch baseline was defined. When a service pack is installed on the server, the patch baseline is set to this service pack.
For more details, please check SharePoint patching demystified
A SharePoint feature pack is a group of new product features and functionality updates that were requested by customers.
SharePoint 2016 has two Feature Packs.
- Feature Pack 1 is delivered in November 2016 Public Update for SharePoint Server 2016 that contains the following features:
- Administrative Actions Logging
- MinRole enhancements
- SharePoint Custom Tiles
- Hybrid Auditing (preview)
- Hybrid Taxonomy (preview)
- OneDrive API for SharePoint on-premises
- OneDrive for Business modern experience (available to Software Assurance customers).
- Feature Pack 2 is delivered in September 2017 Public Update for SharePoint 2016 that contains the following features:
- The foundation of modern web part hosting and editing experiences, including core SPFx APIs, SPFx package deployment, and property panes.
- All the features previously included in Feature Pack 1 for SharePoint Server 2016.
What’s the difference between Feature Pack and Service Pack?
- Service Pack is a tested, cumulative set of all hotfixes, security updates, critical updates, and updates. It mainly concentrates on solving the issue related to the performance, security, and stability of the service.
- Feature Pack is mainly concentrating on the functionality, design changes, and new features that were requested by the customer.
For more details check SPFx for SharePoint Server 2016.
Why: Every Month, Microsoft has been releasing a new update to satisfy their customer requirement by adding new improvements or solving a known security, performance issues.
Therefore, you should follow up the monthly release to recognize the new improvements and the fixed issues to optimize your organization farm.
It’s not recommended to apply the latest Cumulative Update that released in the current month, It was launched a short time ago, no much people try it.
When: Sometimes, you might face an issue in your farm that couldn’t be solved unless installing the appropriate update on your farm.
Therefore, it’s recommended to install the non-security updates that will solve a specific issue in your farm, by checking the improvements and issues that should be fixed before applying the cumulative update. Meanwhile, you should install the latest security updates after they have been released to keep your farm secure.
It’s not recommended to install SharePoint update on production environment until tested on dev/test environment.
Before deciding to download and install a new cumulative update in your SharePoint farm, you should first read carefully the prerequisites section in the release page to know all prerequisites required like the pending CU that should be installed before going ahead to install a new one!
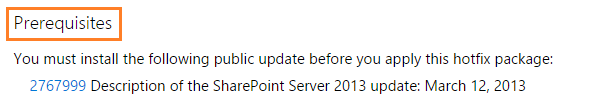
Besides the mentioned instruction in the prerequisites section in the release page, you should take care of the following:
- It’s strongly recommended to install and test the SharePoint update on the dev/test environment before going ahead to install it on the production environment.
- You can’t rollback or uninstall the SharePoint Cumulative Update Installation. so before applying a new cumulative update, It’s strongly recommended to perform a full backup before starting the update process:
- At least you need to perform a backup for the following:
- Content Databases
- Your customization.
- Back up farm configuration by running Backup-SPFarm -ConfigurationOnly.
- At least you need to perform a backup for the following:
- Hot snapshots for virtual machines are NOT supported.
- Only cold snapshots that taken when all virtual machines are shut down are supported.
- The latest security updates should be installed as soon as possible after they have been released.
- After installing the SharePoint security updates, you should plan to run the SharePoint configuration wizard on all SharePoint Servers to apply the new fixes.
- It’s recommended to run first the configuration wizard on the SharePoint server that hosts the central administration.
- It’s also recommended to install non-security updates that will solve a specific issue in your farm by checking the improvements and issues that should be fixed section. (Note: the non-security updates shouldn’t be older than one year even you don’t have an issue in your farm, in our case, we are planning to install it every quarter but and it’s mainly depend on your company policy but at the end it shouldn’t be older than one year).
- It’s not recommended to apply the latest Cumulative Update that released in the current month.
- In SharePoint 2013 and SharePoint 2016 (Without High Availability), you should know that the update process requires downtime, so you should schedule a new RFC with an outage to apply a new patch.
- Zero downtime patching is only supported in SharePoint 2016 and 2019 with a High Availability environment.
- Installing a new language pack requires installing the current installed monthly update again. (In sharepoint 2019 and 2016 only language-dependent fix must be installed again) .
- In SharePoint 2016, each SharePoint installation comes with a language-independent and a language-dependent component. Therefore, It is required to install both (language-independent – language-dependent) fixes to fully patch a SharePoint server (Sequance doesn’t matter)!
- In SharePoint 2013, SharePoint Server 2013 SP1 is a prerequisite to installing all the coming cumulative updates.
- The SharePoint Server 2013 Service Pack 1 does not include the Language pack Service Pack 1, So you should apply Language pack Service Pack 1 separately after applying SharePoint Server 2013 Service Pack 1 to avoid this error. The expected version of the product was not found on the system.
- In SharePoint 2013, the farm with a cumulative update older than April 2018 is not supported.
- SharePoint patching sometimes can take several hours, so try to reduce the update time by checking SharePoint 2013 Cumulative Update takes a long time to install.
The SharePoint should be updated through three steps:
- Download and Install the package update like CU, Service Pack, PU …etc.
- As I elaborated before, you can download the corresponding release of the farm build by clicking on KB number e.g.,”2817429″ to get more details about the release like description, Improvement, Known Issues, Download link and prerequisites.
- Run the SharePoint Configuration Wizard to apply the installed patches on all SharePoint Server cross the farm.
- Check Upgrade Status.
You should make sure that you have already performed a full backup before starting the update process because you can’t rollback the Cumulative Update Installation.
To apply the installed SharePoint patches, you must run SharePoint Configuration Wizard on all SharePoint Server cross the farm by doing the following:
You must remove WSS_Logging database from the Availability Group before running SharePoint Configuration Wizard.
For more details, Please check , The operation cannot be performed on database because it is involved in a database mirroring
Steps
- Log in to the main application server that hosts the Central Administration with a Farm account.
- Go to Start menu > Type SharePoint Configuration Wizard.
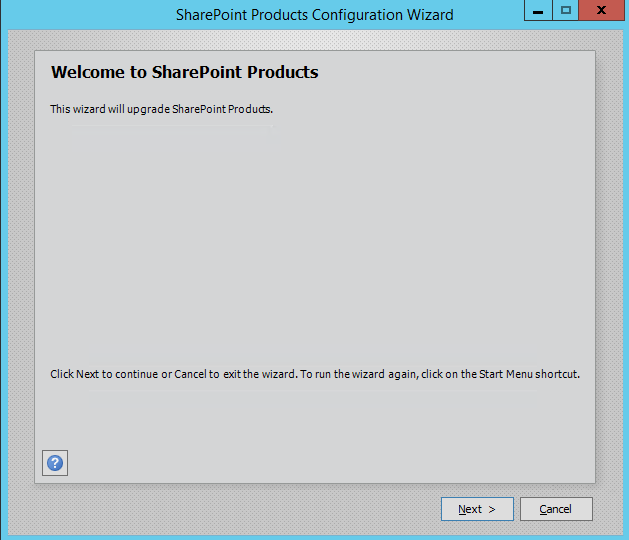
- In step 9, you will note that it’s performing an upgrade to SharePoint Products.
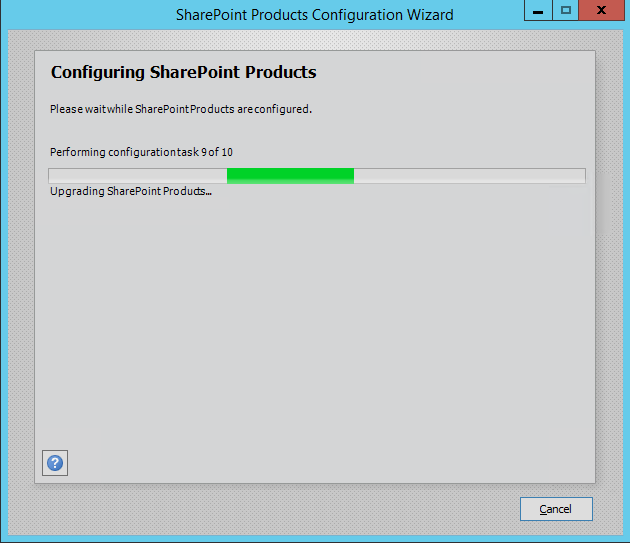
Start to run the SharePoint Configuration Wizard on the main application server that hosts the central administration. then continue with other servers without order.
For more details check Health Analyzer Issue: Product/patch installation or server upgrade required
In some cases, you may need to run SharePoint Configuration Wizard with specific parameters, in this case, you should use PowerShell as the following:
Steps
- Log in to the main application server with a Farm account.
- Open SharePoint Management Shell as Administrator.
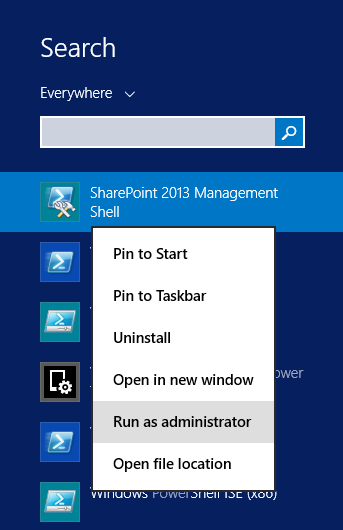
- Run the following PSConfig.exe command
PSConfig.exe -cmd upgrade -inplace b2b -force -cmd applicationcontent -install -cmd installfeatures- Repeat all the previous steps on all SharePoint servers in the farm.
Running the SharePoint configuration wizard requires downtime, so you should a schedule a new RFC with an outage to apply the SharePoint patch!
Once the SharePoint Configuration Wizard is finished successfully on each SharePoint Server cross the farm, you should check SharePoint Upgrade Status by doing the following:
Steps
- Go back to the Central Administration > Upgrade and Migration > Check upgrade status.

- Ensure that the status of each server is succeeded.
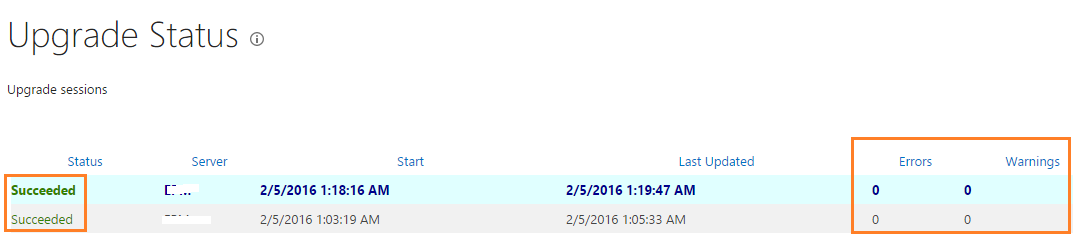
Recall: you can’t rollback the Cumulative Update installation, and
– If the previous upgrade attempt has failed, you must resolve upgrade issues before proceeding to apply a new upgrade.
– If the upgrade process failed, you should check the logs and try to solve the root cause of the failure. In the worth case, you don’t have other options rather than restoring the farm backup.
In SharePoint 2016, each SharePoint installation comes with a language-independent and a language-dependent component. Therefore, It is required to install both (language-independent – language-dependent) fixes to fully patch a SharePoint server!
So to install new Cumulative Update in SharePoint 2016, you should do the following:
First, In any case (Only SharePoint 2016 or SharePoint 2016 with Language Pack), you must do the following:
- It’s mandatory to install both (language-independent – language-dependent) fixes, the sequence does not matter!
- After installing both fixes, you must run the Sharepoint Configuration Wizard on all SharePoint servers cross the farm to apply the installed fixes!
To install a new Language Pack later on SharePoint 2016 farm that already patched with a specific CU, you should do the following:
- Install the new Language Pack.
- Install the language-dependent fix of the current CU installed again!!
- Run the Sharepoint Configuration Wizard on all SharePoint Servers within the farm.
Note: If additional language packs are added later, you will ONLY need to apply the language dependent fix again.
- Zero downtime patching requires the high-availability of each server role at least two servers per role is required.
- There is no zero downtime patching on a single server farm.
- The Zero patching is introduced only in SharePoint 2016, the SharePoint 2013 does not support the Zero downtime patching.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we have learned how to find SharePoint Farm Build Version and Patch Level to find What’s the current Cumulative Update installed on SharePoint Farm?
Also, we have explored the best practices to patch SharePoint farm.
Applies To
- SharePoint 2016.
- SharePoint 2013.
- SharePoint 2010.
Have a Question?
If you have any related questions, please don’t hesitate to ask it at deBUG.to Community.


Pingback: The Project could not be saved to the server In Project Server | SPGeeks
Pingback: This User Profile Application's connection is currently not available | SPGeeks
Finally I have found something which helped me.
Amazing article.
this what i need thank you